

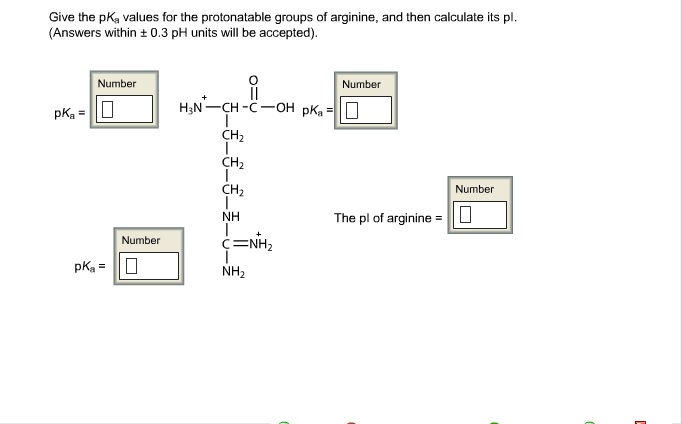
(this is old code so fairly naive, and not well cleaned, but additionally you can find there GUI for windows, some tips for implementation etc.). At the beginning it was written in C++, and in given link some information with sourcesĬode is available for educational purposes If you are interested in the implementation site of IPC, the old version can be accessed here. More advanced algorithm, implemented in ProMoST, takes into account localization of the charged amino acid: aaĪdditionally different pK values are used for N and C terminus depending on uncharged amino acid if applicable: Our pi prediction tool (11) is designed to calculate charge based on the side chains and carboxy- and amino-termini. Each source gives different pKs.ġ Arg was not included in the study and the average pK from all other scales was takenĢ NH2 and COOH were not included in the study and they were taken from Silleroģ Bjellqvist model include also different pK values for terminal residues Unfortunately, there is no agreement in this matter. and glutamic acid, are negatively charged and three amino acids, lysine. Isoelectric point determination is usage of appropriate pK values. The protein isoelectric point (pI) can be calculated from an amino acid. Nevertheless, one can approximately calculate protein isoelectric point which is ± 0.5 of exact isoelectric point. a value of 100 relative to glycine, which is considered neutral (0 value). Therefore, they will become cystines, which do not express any charge. Threonine, Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Arginine, Histidine, Lysine. Lets have these few amino acids as examples: alanine, cysteine and lysine.

Which can oxidise and form disulfide bond in protein. to draw the zwitterion and calculate the isoelectric point of an amino acid. Problematic is also the occurrence of cysteines (negative charge) It is mainly because many proteins areĬhemically modified (amino acids can be phosphorylated, methylated, acetyleted etc.), which change their charge. The result will be almost surely different than real isoelectric point. Using above formulas, we can calculate theoretical isoelectric point. In situation when the gel pH and the protein isoelectric point are equal, proteins do not move at all. Higher than protein isoelectric point, the particles will migrate to the anode (negative electrode) and if the buffer pH is lower than isoelectric point they will go to the cathode. For example, during electrophoresis, direction of proteins migration, depends only from their charge.
Generally, macromolecules are positively charged and on the other hand, above proteins isoelectric point,


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
